
What is EV Charging and How Does it Work?
As a new electric vehicle (EV) owner, one of your major concerns must be when and how to charge your car battery.
Having driven gasoline powered cars all your life and filling up at your local gas stations when the gauge was almost empty, electric car charging is a foreign concept.
Unlike gassing up, EV charging requires more than just pulling in and pumping up. Because it stores electricity in a large battery pack to power its electric motor, you'll have to plug its inlet (essentially, its "gas tank") via EV chargers.
The same concept is implemented in plug in hybrid cars, but they use both battery to power an electric motor and gasoline to power an internal combustion engine.
But once you learn the ropes, you may find it's actually much MORE convenient filling up your old ICE vehicle, especially with rising fuel costs.
We're here to answer what EV charging is and how it works.
What is an EV charger?

Technically, EV chargers are called electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE). It's used to charge both electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids, just like your normal, run-of-the-mill rechargeable devices.
While filling up a conventional internal combustion engine merely takes a few minutes, charging electric cars could take longer.
But with ongoing developments in the electric vehicle industry, it won't be long before electric car drivers enjoy ultra-fast charging with rapid chargers.
Different types of chargers
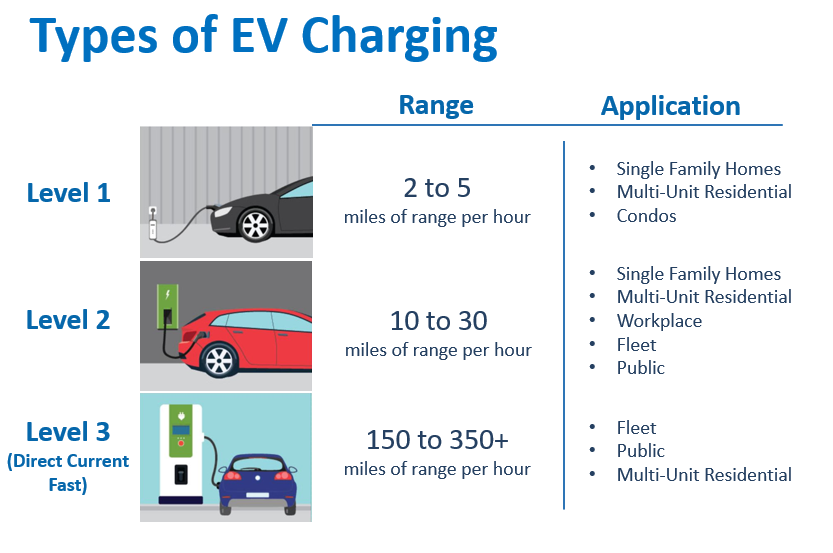
Level 1 EV Charger
A Level 1 charging station is the simplest and has the slowest charging speed of the three. Most EVs come with a Level 1 electric car charger, which you can simply plug into your standard outlet.
Although it is convenient and affordable, the downside is that this charging cable operates on 110-120-volt AC power, resulting in slower charging speeds.
However, with an added 4 to 6 miles of range per hour, it will likely be enough for your daily commute.
If you have an EV with 200 miles of range, it will take around 35 to 50 hours to fully charge.
Level 2 EV charger
Level 2 charging uses connectors that are plugged into 220-240-volt outlets that are typically used for washing machines, electric clothes dryers, and other major appliances. The Tesla wall connector and Lectron V-BOX are an example of Level 2 chargers.
There are portable ones that you can just plug directly into a three-pronged outlet.
You probably have the outlet and circuit in your laundry room, but unplugging your washing machine every time your vehicle’s battery needs a recharge could be inconvenient.
Because of this, many EV drivers opt to install a Level 2 home charging station in their garage.
You’ll need the service of a professional electrician to install a 240-volt dedicated circuit to supply electrical current in your garage.
Such a circuit will let you hardwire your own charging station at home, but the 240-volt socket will also let you plug in a portable unit.
Though electrical upgrades could be costly, Level 2 chargers are significantly faster than Level 1 chargers.
These chargers are very reliable and can give your electric vehicles up to 200 miles of driving range in under 10 hours, so you’ll likely save money in the long run.
DC fast charging
DC fast charging uses direct current (DC power) instead of alternating current.
These DC fast chargers bypass the onboard charger to deliver DC power directly to your car, with up to 400-900V of maximum power.
This can charge your unit from zero to 80% in just under 30 minutes!
All EVs sold in North America use the Combined Charging System connector for DC charging.
In the case of Tesla vehicles, they have proprietary Superchargers with a charging power of up to 250 kW, which can fill up your Tesla model in just 20 minutes.
Because of the amount of energy needed, these types of EV charging stations aren't usually found in residential areas.
Depending on your location, you may find a public charging station that can handle this level of charging.
You can use the phone app to search for public charging stations.
How does EV charging work?
An EV charger pulls electrical current from either a 240-volt outlet or the electric grid it's hardwired to and delivers electricity to your electric vehicle, just like any other device you plug into your wall outlet.
What are the different levels of electric vehicle charging?

There are three levels of electric vehicle charging: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging.
The first two levels use an AC charging system, while DC charging uses direct current (DC).
Level 1 uses a standard wall outlet. Of the three levels, it has the lowest cost to charge, as it doesn't require a dedicated circuit and uses 110-120-volt AC power found in homes.
However, it's also the slowest charging of the three, limited to just 4 to 6 miles of range per hour.
Level 2 charging uses a 240-volt outlet that we usually use for dyers, washers, and air-conditioning. You can either plug it directly or have it hardwired. The portable ones can charge at 40 amps, while the hardwired ones can go up to 48 amps.
Depending on your car's battery capacity, it will take just under 10 hours to fully charge an EV using these AC charging stations.
Level 2 chargers are the top choice when installing charging stations at home, as it's suitable for overnight charging. These can also be seen in public charging stations, as well as in offices, shopping centers, malls, and parking spaces.
DC fast chargers, as the name suggests, use direct current to charge electric vehicles. DC charging stations can deliver up to 400-900V of maximum power. This can charge your car from zero to 80% in just under 30 minutes.
Because of the incredible power it requires, a DC fast charger cannot be used as a home charging station. You'll often see these in commercial EV charging stations. If you're lucky, you may stumble upon a public charging station that offers free chargers for the first 30 minutes. Some paid chargers have a fixed hourly or per kilowatt rate, while others will only ask for a parking fee.
How long does it take to charge an EV?
How long it takes to charge and electric vehicle will depend on the type of charging point you're using and the battery electric vehicles have.
A Level 1 EV charger is limited to just 4 to 6 miles of range per hour, which could be enough for your daily commute. If you have an electric car with a 200-mile range, it will take around 35 to 50 hours to fully charge.
Level 2 EV charging station is the top choice for EV drivers for a home charging session because it uses 220-240-volt outlets that can supply up to 60 amps of power. These EV charging stations can give your electric vehicle up to 13 to 75 miles of range per hour. A full charge is possible in under 10 hours.
DC fast charging stations can give electric vehicles up to 400-900V. This EV charging station can charge your electric car from zero to 80% in just under 30 minutes.
The weather also affects charging speed. EV batteries take longer to charge during colder days as they have to maintain an operating temperature
How do public EV charging stations work?
If you plan on using EV charging stations to top up your car EV's battery, there are a few things you'll need to keep in mind.
An EV charging station may be free to use, or it may require a key fob or other access devices. Some may require credit card payment.
Parking spaces in malls, supermarkets, and offices may offer free charging for customers.
There are also charging memberships offered by commercial EV charging stations for discounted prices.
Not all chargers can fit your EV - but adapters can help
The J1772 plug is the commonly adopted standard for electric vehicles across North America and Canada.
As for Tesla, it has its proprietary charger that only Tesla EVs can use.
So, initially, only non-Tesla EVs had access to J1772 chargers, including the ultra-fast DC charging stations, while Tesla EVs had to stick with their own form of connector.
That's until the introduction of adapters.
J1772 to Tesla adapters greatly increased the number of charging destinations for Tesla drivers.
While Tesla has its own Supercharging network for rapid charging, they're greatly outnumbered by CCS fast charging stations.
But thanks to CCS charger adapters for Tesla, Tesla owners can now access over 5,000 CCS fast chargers nationwide.
When it comes to Level 1 and Level 2 charging, in some areas like California, Tesla charging stations may be more available than J1772 chargers.
Luckily, there are Tesla to J1772 adapters that allow non-Tesla EVs access to more than 15,000 Tesla charging stations across the country.
Do note, though, that these adapters are only compatible with the Tesla High Powered Wall Connectors, all generations of Destination Chargers, and Mobile Connectors.
How to charge an electric car at home
Most electric vehicles already ship with a Level 1 electric car charger included, except for Tesla, which stopped including one starting April this year.
These chargers can be plugged into your standard home outlet. Though convenient, they offer very slow charging.
An overnight charge may give you enough juice for a short commute, but a full charge will take more than a day.
You may want to install a Level 2 charger at home to fully optimize your car’s power. You may purchase one from your car dealer or check out EV charger manufacturers like Lectron for more options.
Such chargers are significantly more powerful than Level 1 chargers and can fill up your car’s battery overnight.
Level 2 chargers are plugged into the same outlet you use for your bigger appliances (think air conditioning units, washers and dryers), so you’ll need to call a licensed electrician to install one.
For example, the Lectron V-BOX is a Level 2 charging station that provides up to 240V and 48A of power. It charges at 11.52 kWh and can fully charge an EV at home in less than six hours.
How does the cost of charging compare to gasoline?
With a current average gas price of $3.28 a gallon, it would cost around $45 to fill up a 12-gallon car tank.
For a car that gets 30 miles of range per gallon, a full tank would give it 360 miles of range.
Driving an average of 1,183 miles per month means having to refuel more than three times a month and spending around $144.
In comparison, driving the same range with an electric vehicle would only cost about $59.15. That's a 40% increase!
Primary factors influencing EV charging
There’s no fixed rate for charging an electric vehicle. The cost will vary depending on several factors. Here are some of the things you should consider for maximum EV savings:
State of charge and depth of discharge
Depth of Discharge (DoP) helps you know how much of your EV’s battery capacity can be used and how long it will last. DoP refers to the amount of battery that has been discharged relative to the total electrical energy supply available. To put it into perspective, discharging 16 kilowatt hours from a 40-kilowatt hour EV battery means the DoP is 40% (16 kWh / 40 kWh).
State of Charge (SoC) is the complete opposite. It refers to the percentage of batteries still available for use. Using our example earlier, a 40 kWh EV battery with a 40% DoP has a state of charge of 60% or 24 kWh.
Amperage
The amperage matters during a charging process if you want to maintain a healthy battery. Most batteries used in electric cars can handle up to 32 amps.
A 32-amp charger can give your car battery up to 25 miles of range per hour.
An average deep cycle battery has a voltage of 12, but this doesn't necessarily mean that you can just grab any 12-volt car charger and assume it can be fully charged safely.
If the charger exceeds 10% of the Amp-hour rating or capacity of your battery, you run the risk of overheating it. The amps can make or break your car's battery.
Investing in a smart charger can save you money in the long run. These chargers communicate with your car, the charging operator, and your utility company through data connections. This optimizes your energy consumption and costs.
FAQs
-
An EV charger pulls electrical current from either a 240-volt outlet or the electric grid it's hardwired to and delivers electricity to your electric vehicle, just like any other device you plug into your wall outlet.
-
There are three levels of electric vehicle charging: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging. The first two levels use an AC charging system, while DC charging uses direct current (DC).
-
All EVs sold in North America use the SAE J1772 connector or the J-Plug for Level 1 and Level 2 charging (besides Tesla/NACS), while the Combined Charging System (CCS) connector is the standard for DC charging.
Tesla has its own proprietary chargers, but these (except Superchargers) can be used by non-Tesla EVs using Tesla to J1772 adaptors.
-
Level 1 chargers can be plugged into a regular 120V outlet. Level 2 chargers use 220-240-volt outlets that are typically used for washing machines, electric clothes dryers, and other major appliances.
-
No, an EV charger only supplies power to your EV battery packs.
-
Yes, using a Level 1 charger plugged into your standard wall outlet. Level 2 chargers can be plugged into your 240-volt dryer plug. If you want a Level 2 charging station at home, check if your electrical grid can handle the additional burden.
